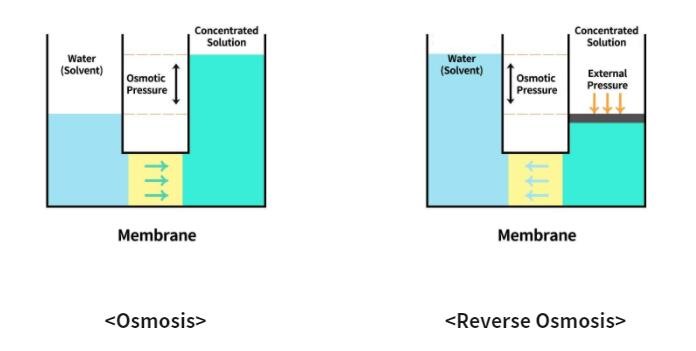
Osmosis is a phenomenon where pure water flows from a dilute solution through a semi permeable membrane to a higher concentrated solution. Semi permeable means that the membrane will allow small molecules and ions to pass through it but acts as a barrier to larger molecules or dissolved substances. Reverse Osmosis is the process of Osmosis in reverse. A solution that is less concentrated will have a natural tendency to migrate to a solution with a higher concentration.
How Does Reverse Osmosis System Work?
Reverse osmosis is a process that removes foreign contaminants, solid substances, large molecules and minerals from water by using pressure to push it through specialized membranes. It is a water purification system used to improve water for drinking, cooking and other important uses..
If there is no water pressure, clean water (water with a low concentration) purified by osmosis will move to the water with a high concentration. The water is pushed through the semipermeable membrane. This membrane filter has a lot of pores, tiny as 0.0001 microns, which can filter about 99% of contaminants such as bacteria (approximately-1 micron), tobacco smoke (0.07 micron_, viruses (0.02-0.04 micron), etc. And only pure water molecules pass through it.
Reverse osmosis water purification may filter out all the useful minerals that our bodies need, but it is an effective and proven technology to produce water that is clean and pure, suitable for drinking. The RO system should provide many years of high purity water, so you can drink it without worries.
Why is a membrane filter effective for water purification?
Generally, the water purifiers that have been developed up to now are largely classified into a membrane-free filter filtration method and a reverse osmosis water purification method using a membrane.
Membrane-free filter filtration is mostly performed with a carbon filter, which filters only the bad taste, odor, chlorine, and some organic substances in tap water. Most particulates, such as inorganic substances, heavy metals, organic chemicals and carcinogens, cannot be removed and passed through. On the other hand, Reverse osmosis water purification method using membrane is the world’s most preferred water purification method using water semi-permeable membrane made by cutting-edge polymer engineering technology. It is a water purification method that passes through and separates and removes various inorganic minerals, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, bacteria, and radioactive materials contained in tap water to make pure water.
The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and the pure solvent is allowed to pass to the other side. To be “selective”, this membrane should not allow large molecules or ions through the pores (holes), but should allow smaller components of the solution (such as solvent molecules, i.e., water, H2O) to pass freely.
This is especially true here in California, where hardness is severe in tap water. So why not enjoy cleaner and safer water with a reverse osmosis system?
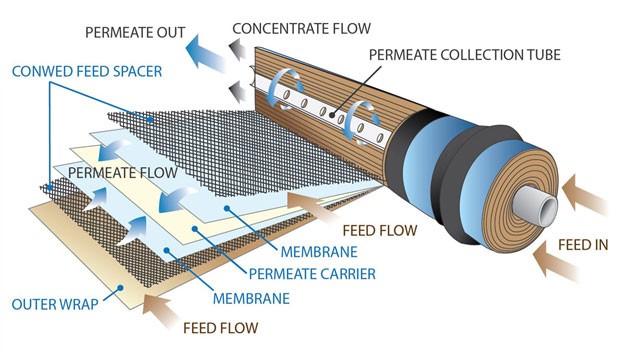
R/O Membrane Filter
In the early 1950s, Dr. Sidney Loeb at UCLA made reverse osmosis (RO) practical by developing, together with Srinivasa Sourirajan, semi-permeable anisotropic membranes. Artificial osmosis membranes are specially designed semi-permeable membranes with pores of 0.0001 microns, one millionth the thickness of hair. This membrane is a special filter made by polymer engineering technology that no chemical contaminants as well as bacteria and viruses can pass through.
When pressure is applied to contaminated water to pass through this special membrane, high molecular weight chemicals, such as limewater dissolved in water, and high molecular weight chemicals such as lime, dissolved in water, are passed through the semi-permeable membrane with only pure water of small molecular weight and dissolved oxygen and traces of organic minerals. They are designed to be discharged out of the membrane by the pressure of new water that does not pass through the semipermeable membrane and continues to push in.
The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and the pure solvent is allowed to pass to the other side. To be “selective”, this membrane should not allow large molecules or ions through the pores (holes), but should allow smaller components of the solution (such as solvent molecules, i.e., water, H2O) to pass freely.
Membranes, which were launched for medical purposes, developed for military warfare or to provide soldiers with clean, uncontaminated drinking water, and further purify the astronaut’s urine collected when unforeseen events occur during space exploration. It is being used for aerospace for drinking water, and recently, major beverage companies are using large-capacity industrial water purifiers for the production of bottles, and are widely used for household water purifiers.
Post time: Jul-04-2022